Pakistan Redeploying Troops to Indian Border
BY Herschel SmithPakistan is beginning troops movement away from the North West Frontier Province towards the border with India.
Pakistan began moving thousands of troops from the Afghan border toward India, officials and witnesses said Friday, raising tensions between the nuclear-armed neighbors and possibly undermining the U.S.-backed campaign against al-Qaida and the Taliban.
The country also announced that it was canceling all military leave in the aftermath of last month’s terror attack on the Indian financial capital of Mumbai.
Glenn Reynolds speculates that this is the effect that the Mumbaiattacks were intended to produce. Most certainly so, and The Captain’s Journal forecast this effect one month ago.
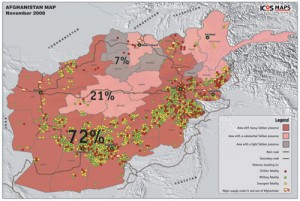
While the new Pakistan administration sees the need for the war against the Taliban and al Qaeda, the Pakistan Army mostly doesn’t and wishes not to be fighting their own people. The Army also has an almost pathological preoccupation with India, and the rumblings in India over the Mumbai attacks have given both the Pakistan Army and the Tehrik-i-Taliban the perfect cover to end their cooperation with the U.S. and NATO over the Taliban safe haven in the Pakistan FATA and NWFP.
This has long term ramifications for the campaign in Afghanistan, but the most serious ramification is a short term one having to do with lines of logistics. Recent large scale attacks on NATO supply lines through Khyber (in Peshawar) were newsworthy for their magnitude and scope, but the chronic persistence and results of these attacks is the important story.
For NATO the most serious problem is not even the depots in Peshawar but the safety of the road that winds west to the 3,500-foot Khyber Pass. The route used to be relatively secure: Afriditribesman were paid by the government to safeguard it, and they were subject to severe penalties and collective tribal punishment for crimes against travelers.
But now the road is a death trap, truckers and some security officials say, with routine attacks like one on Sunday that burned a fuel tanker and another last Friday that killed three drivers returning from Afghanistan.
“The road is so unsafe that even the locals are reluctant to go back to their villages from Peshawar,” said Gul Naseem, who lives in Landi Kotal, near the border.
The largest truckers’ association here has gone on strike to protest the lack of security, saying that the job action has sidelined 60 percent of the trucks that normally haul military goods. An American official denied that the drop-off had been that severe.
“Not a single day passes when something doesn’t happen,” said Shakir Afridi, leader of the truckers’ group, the Khyber Transport Association. He said at least 25 trucks and six oil tankers were destroyed this month. “Attacks have become a daily affair,” he said.
This means that the potential logistical supply via Georgia being pursued by the Pentagon takes on urgent importance. The upcoming Obama administration might have to make some tough decisions regarding Georgia. “Georgia is the center of gravity in this plan, and our willingness to defend her and come to her aid might just be the one thing that … saves Georgia as a supply route.”
Russia has thrown down the gauntlet regarding her intended future and what she considers to be her near-abroad. “In the latest of a series of combative moves by the Kremlin, a senior government official in Moscow said the Russian military would commission 70 strategic missiles over the next three years, as part of a massive rearmament programme which will also include short-range missiles, 300 tanks, 14 warships and 50 planes.”
The nexus of Vladimir Putin’s aspirations, the U.S.-led campaign in Afghanistan, and the future of the Russian near-abroad has been all but ensured by the Taliban program to interdict supplies in Khyber, and more specifically by less than a platoon of well-trained teenagers who inflicted terror on Mumbai for three days in late 2008.
Prior:
U.S-Georgia Strategic Partnership
The Logistical Battle: New Lines of Supply to Afghanistan
The Search for Alternate Supply Routes to Afghanistan
Large Scale Taliban Operations to Interdict Supply Lines
More on Lines of Logistics for Afghanistan
How Many Troops Can We Logistically Support in Afghanistan?
Targeting of NATO Supply Lines Through Pakistan Expands
Logistical Difficulties in Afghanistan
Taliban Control of Supply Routes to Kabul

 .
.